Noble metal-metal oxide nanohybrids with tailored nanostructures for efficient solar energy conversion, photocatalysis and environmental remediation
Liu, Xueqin;Iocozzia, James;Wang, Yang;Cui, Xun; Chen, Yihuang;Zhao, Shiqiang; Li, Zhen*;Lin, Zhiqun
ENERGY & ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCE,Volume 10,Issue 2,15 February 2017,Pages 402-434
DOI: 10.1039/c6ee02265k
Abstract:
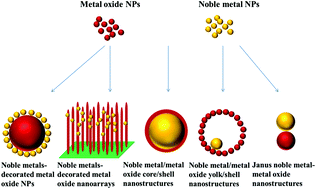
The controlled synthesis of nanohybrids composed of noble metals (Au, Ag, Pt and Pd, as well as AuAg alloy) and metal oxides (ZnO, TiO2, Cu2O and CeO2) have received considerable attention for applications in photocatalysis, solar cells, drug delivery, surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy and many other important areas. The overall architecture of nanocomposites is one of the most important factors dictating the physical properties of nanohybrids. Noble metals can be coupled to metal oxides to yield diversified nanostructures, including noble metal decorated-metal oxide nanoparticles (NPs), nanoarrays, noble metal/metal oxide core/shell, noble metal/metal oxide yolk/shell and Janus noble metal–metal oxide nanostructures. In this review, we focus on the significant advances in tailored nanostructures of noble metal–metal oxide nanohybrids. The improvement in performance in the representative solar energy conversion applications including photocatalytic degradation of organic pollutants, photocatalytic hydrogen generation, photocatalytic CO2 reduction, dye-sensitized solar cells (DSSCs) and perovskite solar cells (PSCs) are discussed. Finally, we conclude with a perspective on the future direction and prospects of these controllable nanohybrid materials. 全文链接

